Inconsistent Surface Registration via Optimization of Mapping Distortions
Project Description:
We
address the problem of registering two surfaces, of which a natural
bijection between them does not exist. More precisely, only a partial
subset of the source domain is assumed to be in correspondence with a
subset of the target domain. We call such a problem an {\it
inconsistent surface registration} problem. This problem is challenging
as the corresponding regions on each surfaces and a meaningful
bijection between them have to be simultaneously determined. In this
paper, we propose a variational model to solve the inconsistent surface
registration problem by minimizing mapping distortions. Mapping
distortions are described by the Beltrami coefficient as well as the
differential of the mapping. Registration is then guided by feature
landmarks and/or intensities, such as curvatures, defined on each
surfaces. The key idea of the approach is to control angle and scale
distortions via quasiconformal theory as well as minimizing landmark
and/or intensity mismatch. A splitting method is proposed to
iteratively search for the optimal corresponding regions as well as the
optimal bijection between them. Bijectivity of the mapping is easily
enforced by a thresholding of the Beltrami coefficient. We test the
proposed method on both synthetic and real examples. Experimental
results demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed model.
Publication:
- S. Di, L.M. Lui, Inconsistent Surface Registration via Optimization of Mapping Distortions, under review (2020)
 (Left)
Moving human face; (Middle) Target static human face; (Right) The
difference of mean curvatures between the registered and target
surfaces on the registered surface. Our algorithm simultaneously
determines the corresponding regions on the two surfaces and the
registration map between them.
(Left)
Moving human face; (Middle) Target static human face; (Right) The
difference of mean curvatures between the registered and target
surfaces on the registered surface. Our algorithm simultaneously
determines the corresponding regions on the two surfaces and the
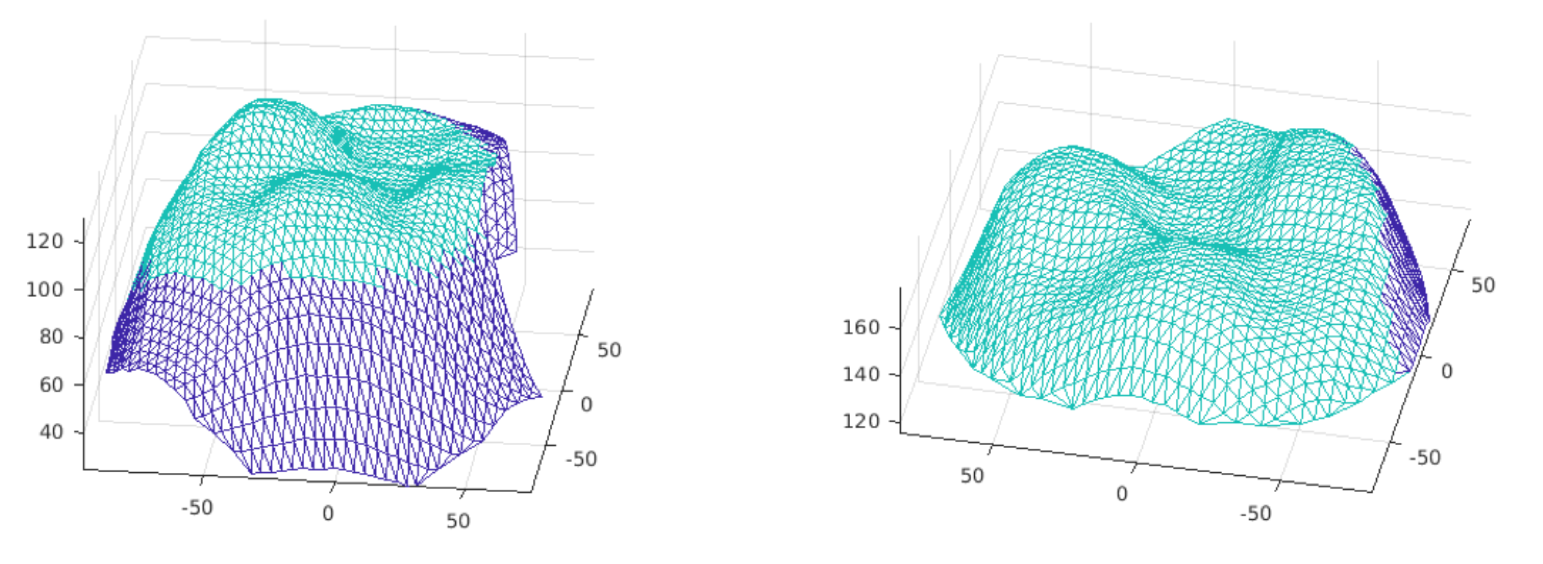
registration map between them.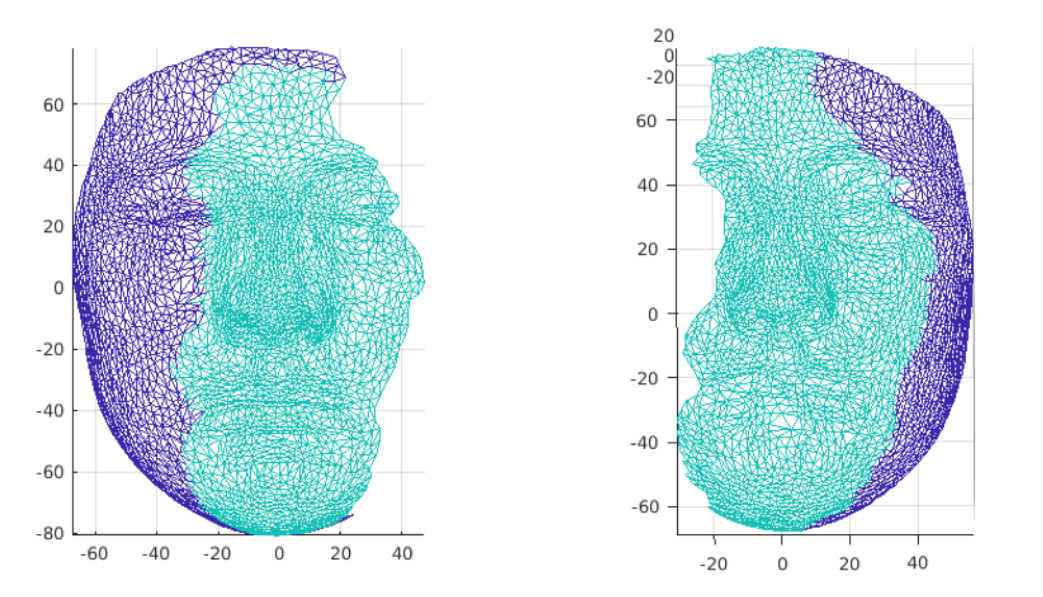
Corresponding regions on the moving and static human faces in the last example. The green region on left showsthe corresponding region on the moving surface. The green region on the right shows the corresponding region on the target surface. Our algorithm simultaneously determines the corresponding regions on the two surfaces and the registration map between them.
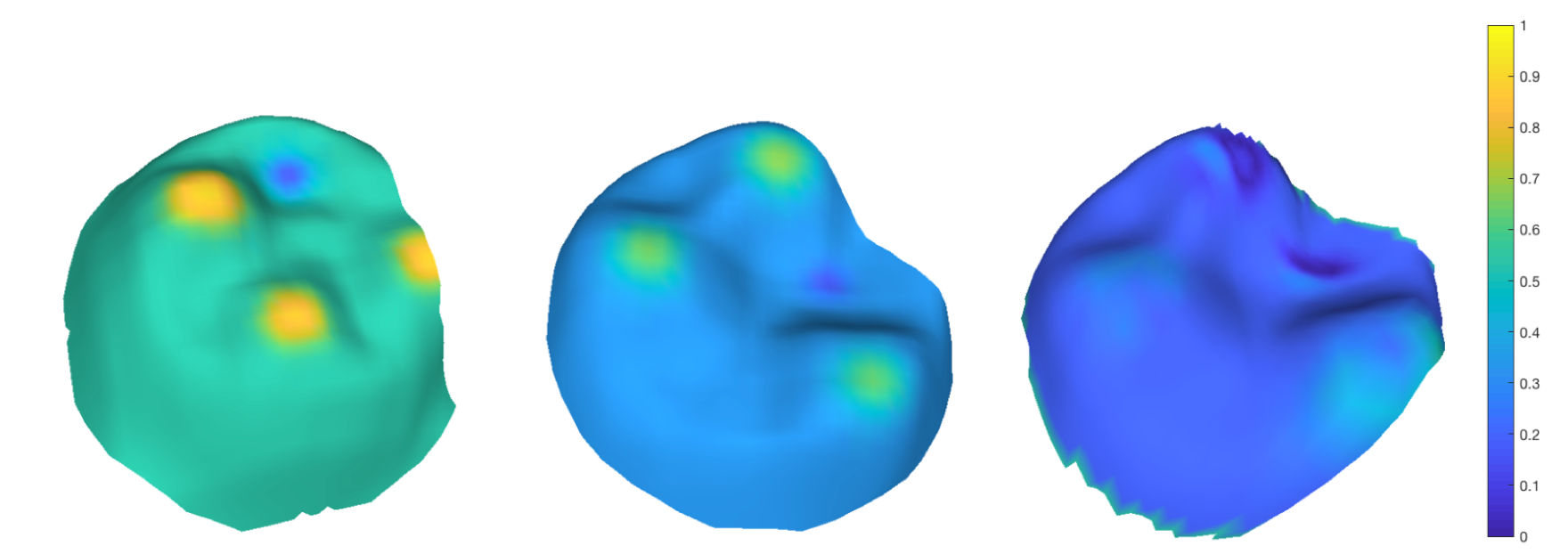
Surface registration for another pair of inconsistent tooth surfaces. The left shows the inputmoving tooth surface. The middle shows the target static tooth surface. The right shows the difference of intensitieson the registered surface.
Corresponding regions on the moving and static tooth surfaces in the last example. The green region on left showsthe corresponding region on the moving tooth surface. The green region on the right shows the corresponding regionon the target tooth surface.